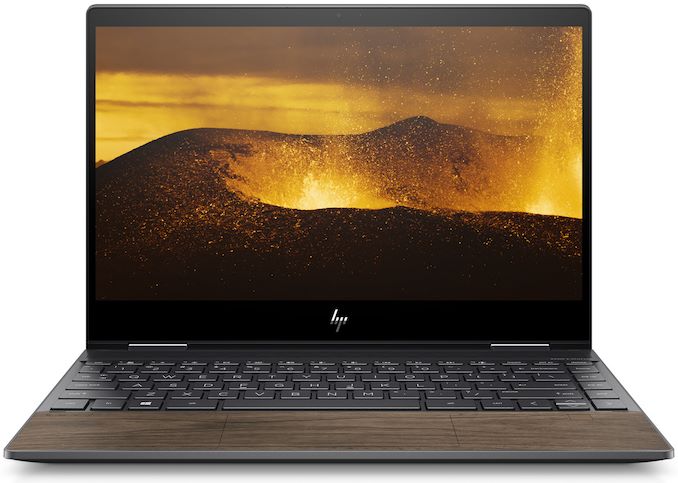
For those more discerning laptop users out there who are on the market for a more exotic laptop design, HP has started sales of its Envy x360 13 Wood Edition convertibles. Featuring a wooden palm rest, the AMD’s Ryzen Mobile 3000-powered laptops are otherwise mainstream-focused laptops aiming for a good balance between size and power, but with some more eye-catching aesthetics. For now, what’s arguably the most stylish AMD Ryzen-powered hybrid PCs are only available in Japan, but it is likely that they will start emerging in the US shortly.
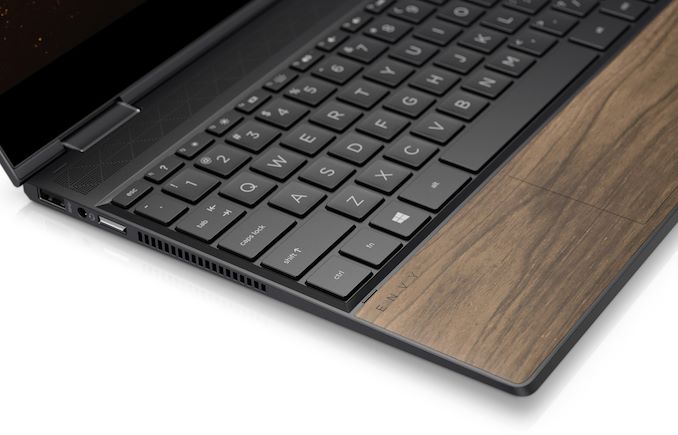

HP’s Envy x360 13 Wood Edition machines come in a sleek metallic chassis with a Nightfall Black or Natural Walnut wooden palm rest. The convertibles are 14.5 mm ~ 16 mm thick and weigh 1.28 kilograms, which makes them the sleekest hybrid notebooks powered by AMD’s Ryzen Mobile APUs to date. The Envy x360 13 Wood Edition convertible laptops feature the company’s signature hinges (tested for 32,000 open/close cycles) as well as house a 13.3-inch Full-HD touchscreen display with thin bezels on three sides.

Depending on exact model, Envy x360 13 Wood Edition convertible laptops are based on the AMD Ryzen Mobile 3000 APUs (up to Ryzen 7 3700U) that are paired with 8 GB or 16 GB of DDR4 memory, as well as a 256 GB or 512 GB M.2 SSD with a PCIe 3.0 x4 interface.
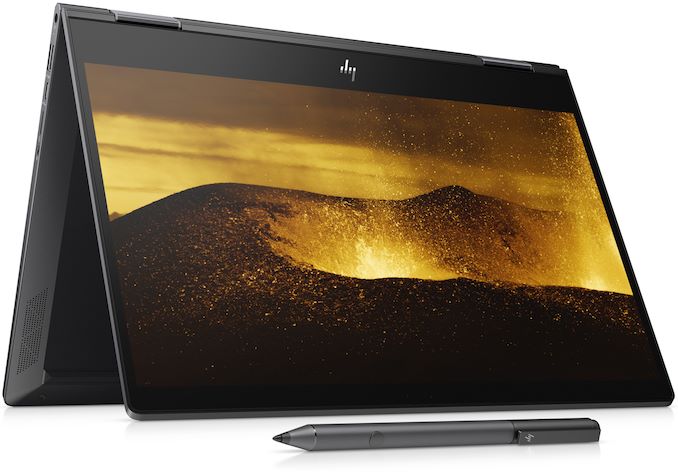

As far as I/O is concerned, the convertible Envy x360 13 Wood Edition comes equipped with Wi-Fi 5, Bluetooth 4.2, one USB 3.0 Type-C port, two USB 2.0/3.0 Type-A ports, and a 3.5-mm jack for headsets. Traditional for modern Envy laptops, the hybrid Envy x360 13 Wood Edition features a fingerprint reader compatible with Windows Hello, a webcam that can be physically disabled using a switch, four speakers co-designed with Bang & Olufsen, and a microphone array.
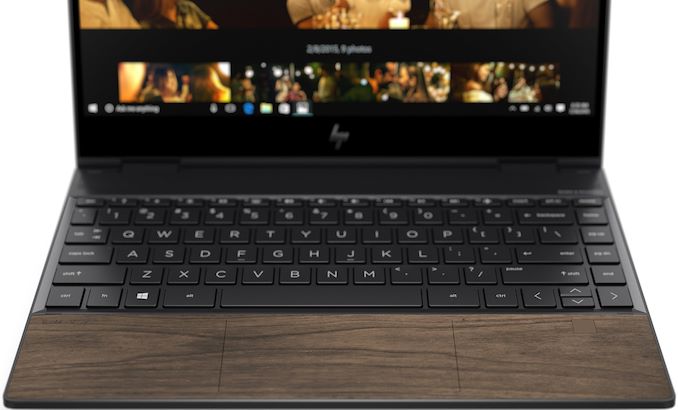

When it comes to battery life, HP promises that the Envy x360 13 Wood Edition is rated to work for up to 14.5 hours, though HP isn’t disclosing the actual battery capacity. Though as things stand, an over 14-hours battery life would make the the hybrid notebooks some of the longest lasting AMD Ryzen-based machines around.
HP’s Envy x360 13 Wood Edition with AMD Ryzen
Japanese Models |
| |
Basic |
Standard |
Standard
Plus |
Performance |
| Display |
13.3-inch 1920×1080 |
| CPU |
AMD Ryzen 3 3300U
4C/4T
6 MB
2.1 – 3.5 GHz
15 W |
AMD Ryzen 5 3500U
4C/8T
6 MB
2.1 – 3.7 GHz
15 W |
AMD Ryzen 7 3700U 4C/8T
6 MB,
2.3 – 4.0 GHz
15 W |
| Graphics |
Radeon Vega 6
384 SPs at 1.2 GHz |
Radeon Vega 8
512 SPs at 1.2 GHz |
Radeon RX Vega 10
640 SPs at 1.4 GHz |
| RAM |
8 GB DDR4 |
16 GB DDR4 |
| SSD |
256 GB PCIe SSD |
512 GB PCIe SSD |
| Wi-Fi |
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
| Bluetooth |
Bluetooth 4.2 |
| USB |
2 × USB 3.0 Type-A
1 × USB 3.0 Type-C |
| GbE |
– |
| Card Reader |
– |
| Other I/O |
microphone, four Bang & Olufsen speakers, audio jack |
| Battery |
up to 14.5 hours |
| Dimensions |
Width: 306 mm
Depth: 212 mm
Thickness: 14.5 mm – 16 mm |
| Weight |
1.28 kilograms |
| Additional Information |
Link |
Price
(w/o tax) |
¥92,800
~$855 |
¥99,800
~$920 |
¥104,800
~$965 |
¥124,800
~$1,150 |
Depending on exact model, HP’s Envy x360 13 Wood Edition convertible laptops are priced between ¥92,800 ($855) and ¥124,800 ($1,150) without taxes. As an added bonus, HP bundles its new hybrid notebooks with a 16 GB USB flash drive from Hacoa that is also made of wood. These drives are produced in Japan, so they may not be bundled with the said PCs in other countries.

Related Reading:
Sources: HP, PC Watch
Source: AnandTech – HP’s Envy x360 13 Wood Edition w/ AMD Ryzen Now Available