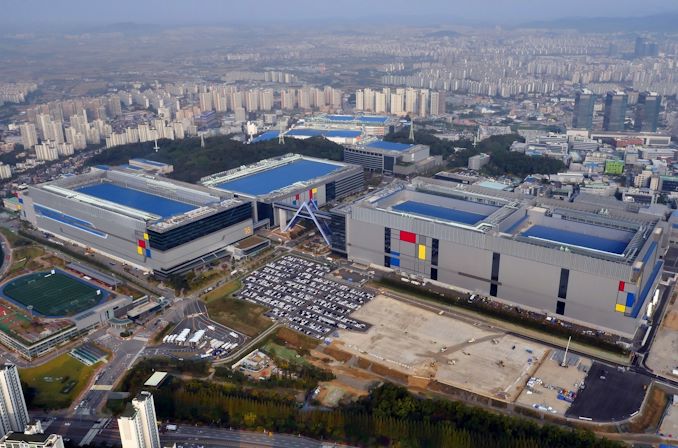
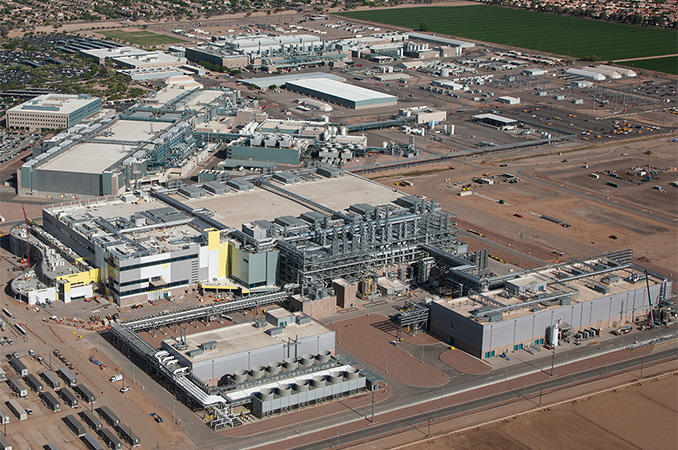
Samsung on Wednesday unveiled their plan to invest $230 billion over the next 20 years in a new semiconductor production mega cluster in South Korea. The country’s government believes that the new chip manufacturing site and the expansion of existing fabs will make South Korea the world’s largest producer of chips, de-throning Taiwan.
“The mega cluster will be the key base of our semiconductor ecosystem,” a statement by the South Korean government published by Nikkei reads. [The mega cluster will enable South Korea to] leap forward as a leading country amid fierce global competition over advanced industries.”
Samsung’s new campus will be located near Yongin, Gyeonggi Province, and will house five advanced fabs. Some of the fabs will be used to produce logic chips for Samsung Foundry’s customers, and others will focus on making various types of memory. Samsung plans to invest some $230 billion in its new site in exchange for tax breaks, subsidies, and other incentives from the government.
$230 billion is a huge pile of money, but it will be spent over a period of 20 years (i.e., $11.5 billion per year if spread equally) and on giant fabs that will use leading-edge fabrication technologies. These production facilities are set to adopt extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography scanners, which are extremely expensive. A current-generation ASML Twinscan NXE scanner with a 0.33 numerical aperture (NA) optics costs around $200 million, whereas a next-generation Twinscan EXE scanner with a 0.55 NA optics (High-NA) is expected to cost about $400 million. Every fab requires several cutting-edge scanners and thousands of other expensive tools to produce chips on leading-edge process technologies, so fabs are getting more costly and will be getting even more expensive in the coming years, so huge investment plans are set to become more common.

In addition to logic and memory chip production facilities, the new mega cluster will also house Samsung’s semiconductor ecosystem partners, including suppliers of raw materials, parts, and even fabless chip designers, a total of 150 companies, reports Yonhap. Ecosystem partners tend to locate their facilities near large fab complexes to simplify logistics, but finding fabless chip developers in the fab campuses is something new. This might make a lot of sense since close collaboration between chip designers and chip producers at all stages may ensure higher performance and faster time-to-yield.
“The mega cluster will have the whole semiconductor value chain,” the ministry said in a release. “The government will implement measures to become a global leader in the system semiconductor industry without a hitch in close cooperation with companies.”
Interestingly, the South Korean government plans to nurture ten fabless firms with annual sales of over 1 trillion won ($761.4 million) by extending support for their prototype production, the Yonhap report reads, citing government officials.
Samsung’s $230 billion investment is a pivotal part of South Korea’s plans to attract some $422 billion of private investments into such sectors as batteries, biotechnology, displays, electric vehicles, robots, and semiconductors over the next few decades.
“The economic war that began recently in semiconductors is broadening to advanced industries such as batteries and cars of the future,” said Yoon Suk Yeol, president of South Korea, in a TV interview, reports Bloomberg. “Each country is sparing nothing in large-scale subsidies and tax benefits to build cutting-edge manufacturing facilities at home.”
Indeed, China, Japan, the European Union, Taiwan, and the U.S. are all trying to advance emerging technologies and industries like AI, autonomous vehicles, high-performance computing, robotics, and renewable energy sources. Computer chips are crucial for all emerging technologies and industries, so Samsung’s new mega cluster fab complex is vital for the company and the country.
![]()
![]()
Source: AnandTech – Samsung Seeks to Make South Korea No. 1 Chipmaker with 0B Investment Over 20 Years