Intel Corp. will not proceed with its $5.4 billion deal to acquire Tower Semiconductor foundry due to a lack of regulatory approval from China, the two companies announced on Wednesday. Instead of renegotiating, Intel will pay Tower a $353 million break-up fee to walk away. The move will force Intel to focus the business strategy of its Intel Foundry Services (IFS) division solely on leading-edge process technologies.
Good Fit
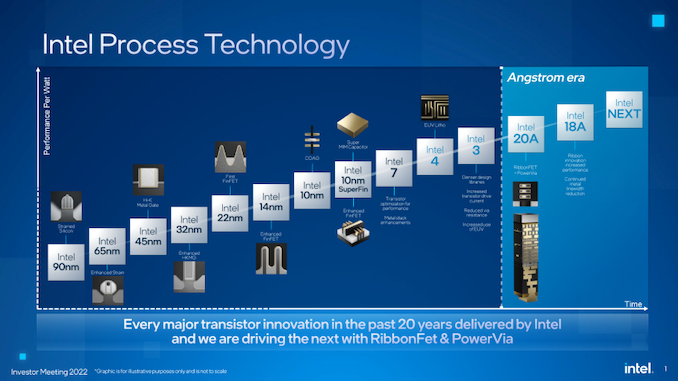
Intel’s business strategy has always relied on building leading-edge and producing the world’s most advanced chips on the most sophisticated production nodes to depreciate fabs while earning hefty margins quickly. As costs of modern fabs got inherently higher than they used to be and R&D costs of process technologies were consistently increasing, Intel needed to expand its production volumes to retain profitability, and offering foundry services was an excellent way to do so.
Since Intel has historically only produced chips for itself, it tailored its process technologies solely for its CPU products. It had to outsource its own GPU and FPGA products manufacturing to TSMC or GlobalFoundries as their technologies were better fit for these types of devices. As a foundry, Intel needed to tailor its nodes for a broader range of applications (which it presumably did with 20A and 18A) and ensure compatibility of its process technologies with commercially available electronic design automation (EDA) and verification tools. But Intel also needed to offer something more than just leading-edge nodes for the most sophisticated chips on the planet.
So, it decided to acquire another contracted chip maker, and Tower Semiconductor seemed like a good fit. Tower’s expertise lies in manufacturing specialized chips, such as mixed-signal, RFCMOS, silicon photonics, PMICs, and more, using specialty and mature process technologies like BiCMOS, SiGe, and SOI at its seven fabs in Israel, the U.S., and Japan. These technologies might not be at the forefront of innovation. Still, they are crucial for applications that are made in huge volumes, have very long lifecycles, and are always in high demand. Therefore, the deal would significantly expand IFS’s client base in the foundry sector and bring onboard experts with vast experience in contract chipmaking.
Re-Focusing Solely to Leading-Edge Nodes
Without Tower, IFS will need to focus on making chips on just a few nodes (Intel 16, 20A, 18A, and Intel 3) and will compete directly with TSMC and Samsung Foundry using only these process technologies. Instead of gaining dozens of customers overnight, IFS will have to work hard to land orders and grow its customer base. Still, the company says it is not dropping its plan to become the world’s second-largest foundry by 2030, thus replacing Samsung from the No. 2 spot.
“Since its launch in 2021, Intel Foundry Services has gained traction with customers and partners, and we have made significant advancements toward our goal of becoming the second-largest global external foundry by the end of the decade,” said Stuart Pann, senior vice president and general manager of Intel Foundry Services (IFS).
This is not going to be particularly easy. IFS’s journey has been filled with ups and downs. IFS’s partnerships with Arm, MediaTek, and the U.S. Department of Defense highlight its growing influence in the sector. Furthermore, Intel’s commitment to building leading-edge fabs and advanced packaging facilities in different parts of the world (Europe, Middle East, North America) emphasizes that the company is looking for clients across the globe and is no longer focused entirely on its own products.
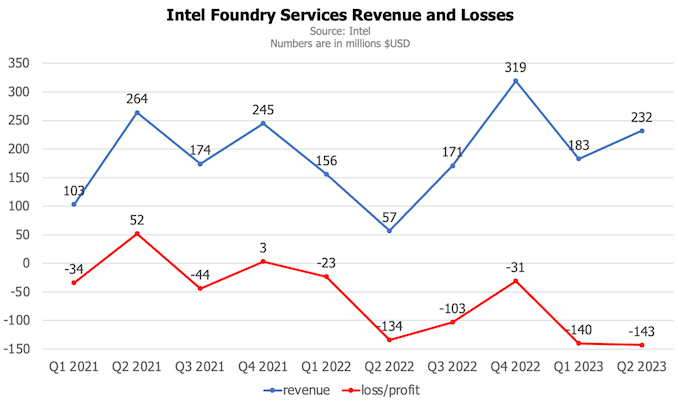
However, the financial side tells a different story. In 2021, Intel’s foundry unit reported revenues of $786 million but faced a loss of $23 million. The following year it reported revenues of $703 million (after adjusting its financial statements for the first two quarters of 2022) and a loss of $291 million. In 2023, IFS has seen revenues of $415 million, marking a 13% increase from the first half of 2021 and a 94% jump from the first half of 2022, but it also reported a loss of $283 million.
By contrast, Tower Semiconductor reported revenue of $1.68 billion in 2022, up from $1.51 billion in 2021. The company’s net profit for 2022 reached $265 million, a 76% surge compared to the $150 million recorded in 2021.
Furthermore, two years since the formal establishment of IFS, only MediaTek has officially committed to using Intel’s advanced fabrication technologies. Large fabless clients tend not to make loud announcements regarding their foundry deals, so IFS may have many high-profile clients waiting to adopt its upcoming nodes but being mum about it to not spoil their current relationships with TSMC and Samsung Foundry.
Key Pillars
But without Tower Semiconductor, its customer base, and experienced management, the mid-term success of IFS will rely on several pillars: Intel 16 fabrication technology aimed at inexpensive chips, Intel 3 manufacturing process that looks to be optimized primarily for datacenter-bound processors, leading-edge 20A and 18A production nodes that promise to be more innovative than competitors, and Intel’s advanced packaging technologies coupled with vast packaging capacities. Intel’s ability to offer vertically integrated services that include wafer processing and chip packaging will also play an essential role in the success of its IFS division.
“We are building a differentiated customer value proposition as the world’s first open system foundry, with the technology portfolio and manufacturing expertise that includes packaging, chiplet standards and software, going beyond traditional wafer manufacturing,” said Pann.
Source: Intel
Source: AnandTech – Intel Calls Off Tower Acquisition, Forced to Focus Solely on Leading-Edge Nodes